Introduction to Hybrid Zucchini Seeds and Hybrid Melon Seeds Production
Hybrid vegetable seeds have revolutionized modern agriculture. For crops like zucchini and melon, hybridization allows farmers to enjoy higher yields, disease resistance, better adaptability, and improved fruit quality compared to open-pollinated varieties.
At the heart of hybrid seed development lies a critical process: cross-pollination. By carefully selecting parent plants and managing pollination, seed producers can create hybrid zucchini and melon seeds that perform exceptionally well across diverse climates and markets.

In this blog, we will explore how cross-pollination works in zucchini and melon seed production, its benefits, challenges, and why it’s key to sustainable agriculture.

hybrid zucchini seeds hybrid vegetable seeds base
Understanding Cross-Pollination in Cucurbits
What Is Cross-Pollination?
Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male flower of one plant to the female flower of another genetically distinct plant. In hybrid seed production, this ensures that the resulting seeds carry a combination of traits from both parents.

For zucchini and melons, which belong to the Cucurbitaceae family, cross-pollination is essential to produce vigorous hybrid offspring with desirable characteristics like uniform fruit shape, sweetness, disease resistance, and high yield potential.
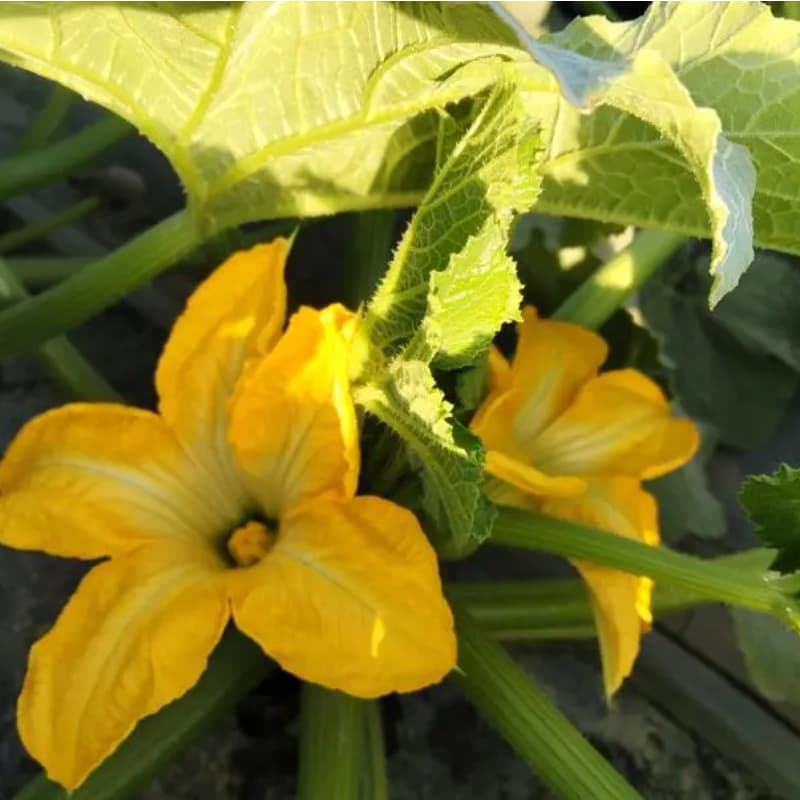
How Zucchini and Melon Flowers Function
Both zucchini and melon plants produce separate male and female flowers.
- Male flowers: Contain stamens that produce pollen.
- Female flowers: Contain ovaries that develop into fruits after pollination.
Without pollination, fruits do not form. In hybrid production, breeders must carefully manage which pollen fertilizes which flower to maintain seed purity.

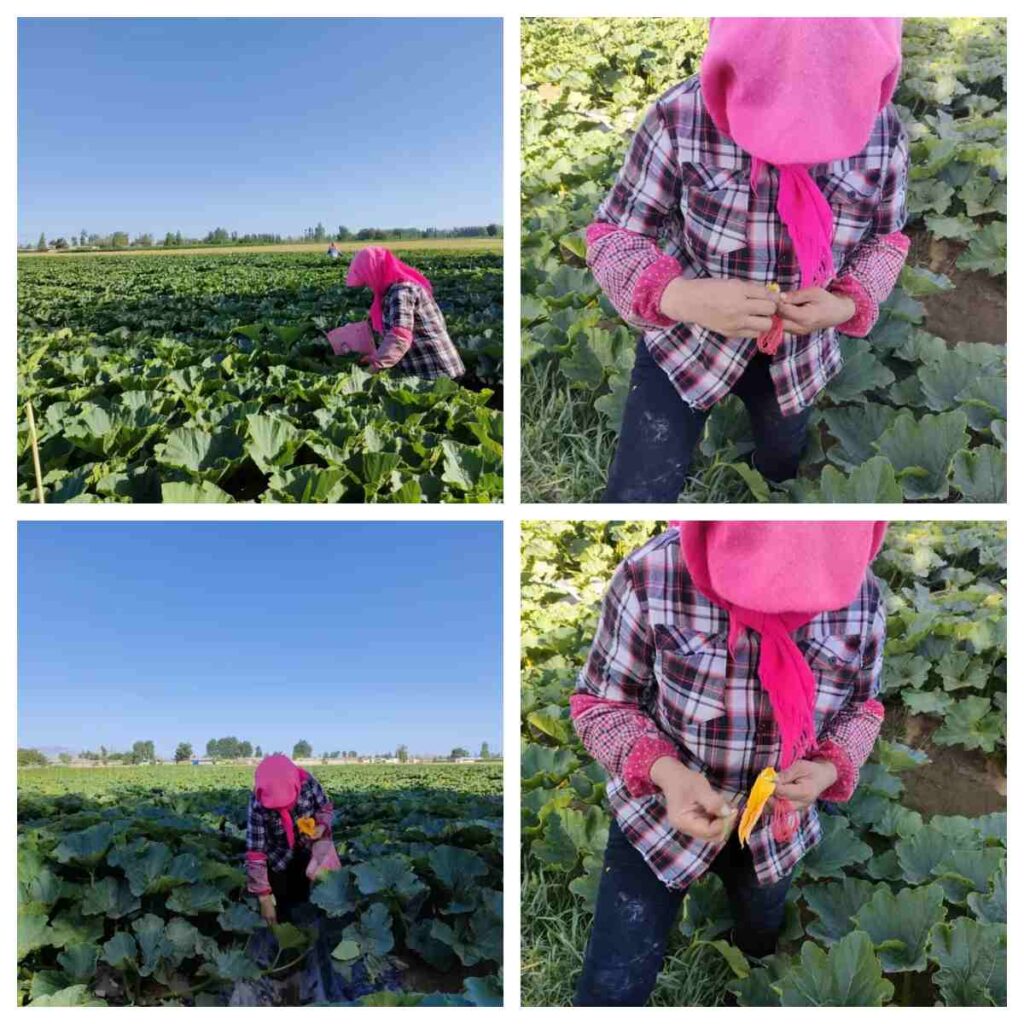
Pollination Methods: Natural Pollinators vs. Manual Techniques
In open fields, bees and insects naturally transfer pollen. However, in controlled hybrid seed production, manual pollination is often required. Workers may hand-pollinate flowers, ensuring that only selected male parent lines fertilize the chosen female plants.
This strict control ensures genetic integrity and maintains the unique qualities of hybrid zucchini and melon seeds.
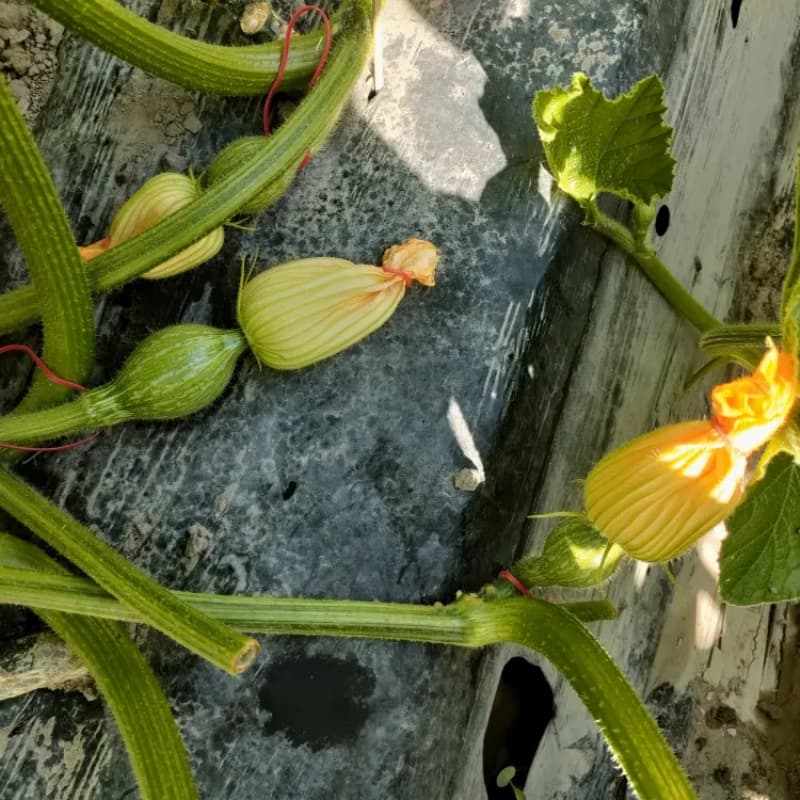

Step-by-Step Hybrid Seed Production Process
Selecting Parent Lines
The foundation of hybrid seed production is the selection of male and female parent lines. Breeders choose plants with complementary traits:
- Disease resistance
- High sugar content (for melons)
- Early maturity (for zucchini)
- High yield potential
- Uniform shape and attractive appearance
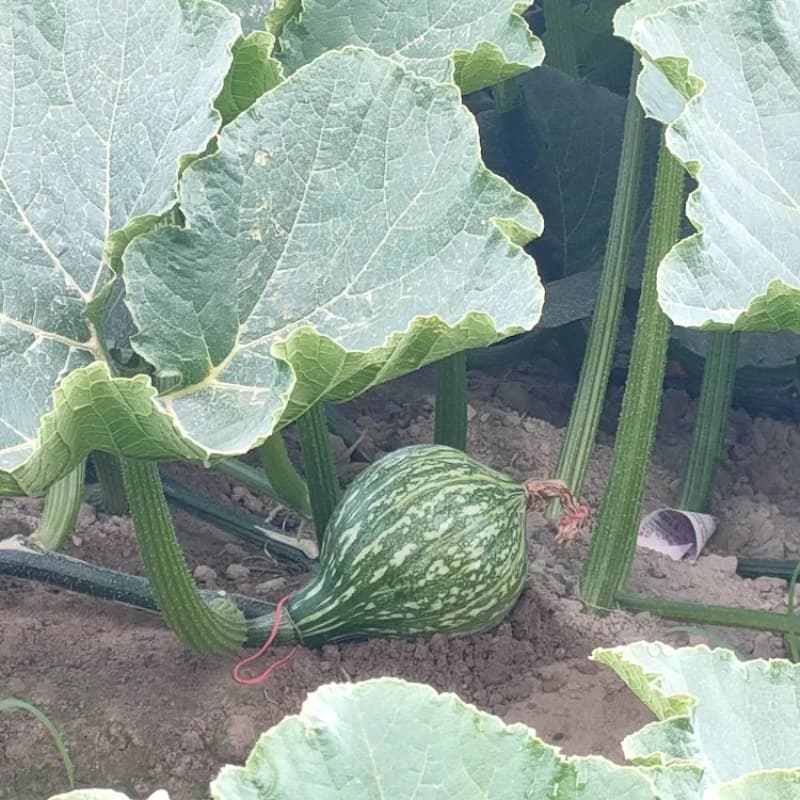

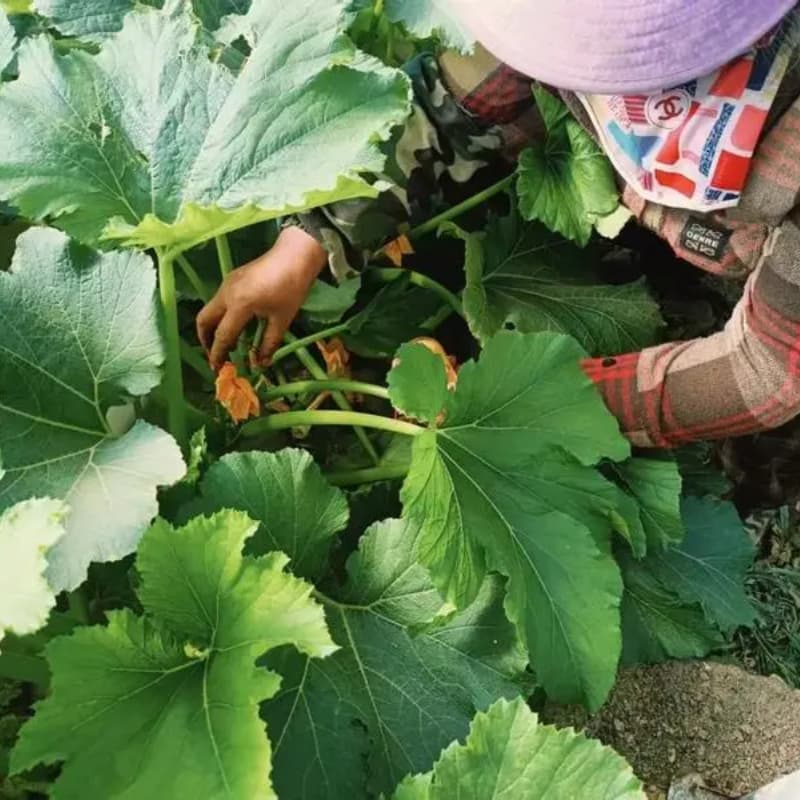
Emasculation and Controlled Pollination
To prevent self-pollination, female flowers are emasculated (removal of anthers). Then, pollen from the chosen male parent is manually transferred to the female flower.
This careful process ensures the seeds produced are true hybrids, carrying the strengths of both parents.
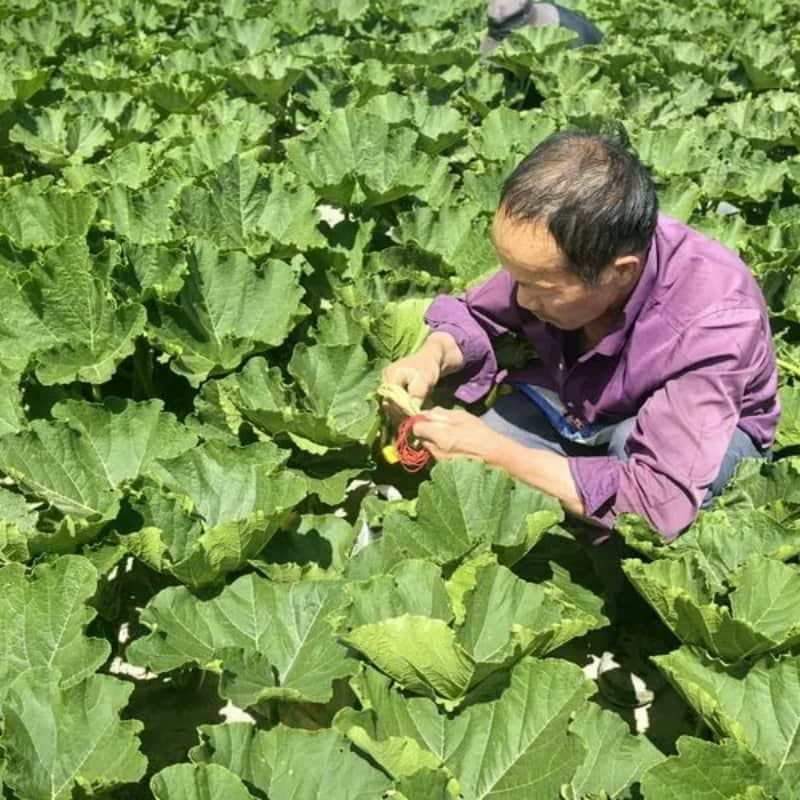

Ensuring Purity in Cross-Pollination
Seed purity is crucial in commercial seed production. Techniques include:
- Isolation distance: Planting hybrid fields far from other cucurbits to avoid unwanted pollen flow.
- Bagging flowers: Covering flowers before and after pollination.
- Controlled timing: Pollinating in early morning hours when flowers are most receptive.
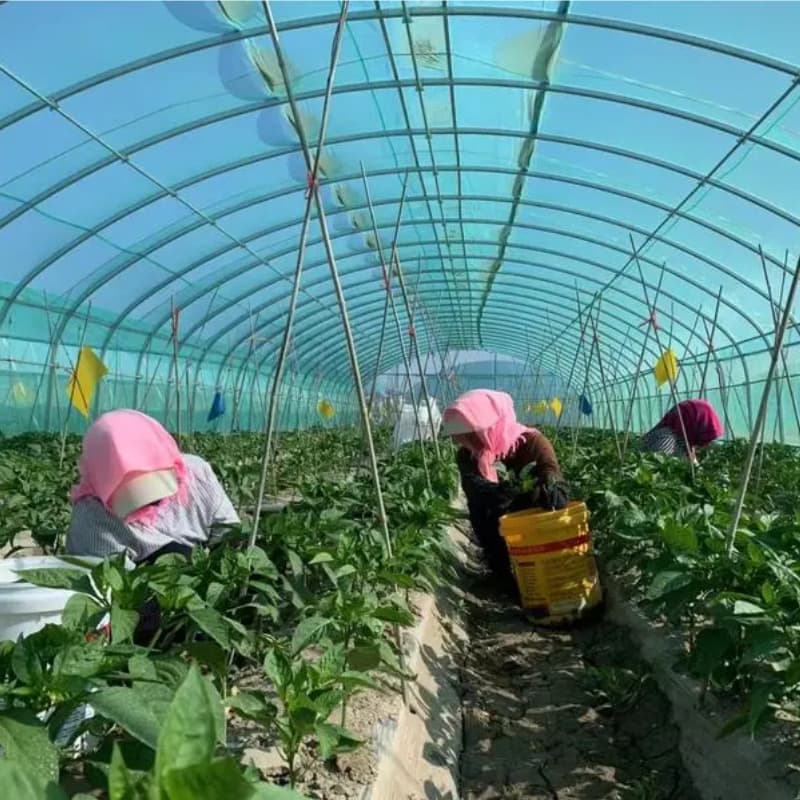

Role of Pollinators
In some cases, managed pollinators such as bees are introduced to fields. However, when precise hybridization is required, manual pollination remains the most reliable method.
Advantages of Cross-Pollinated Hybrid Seeds
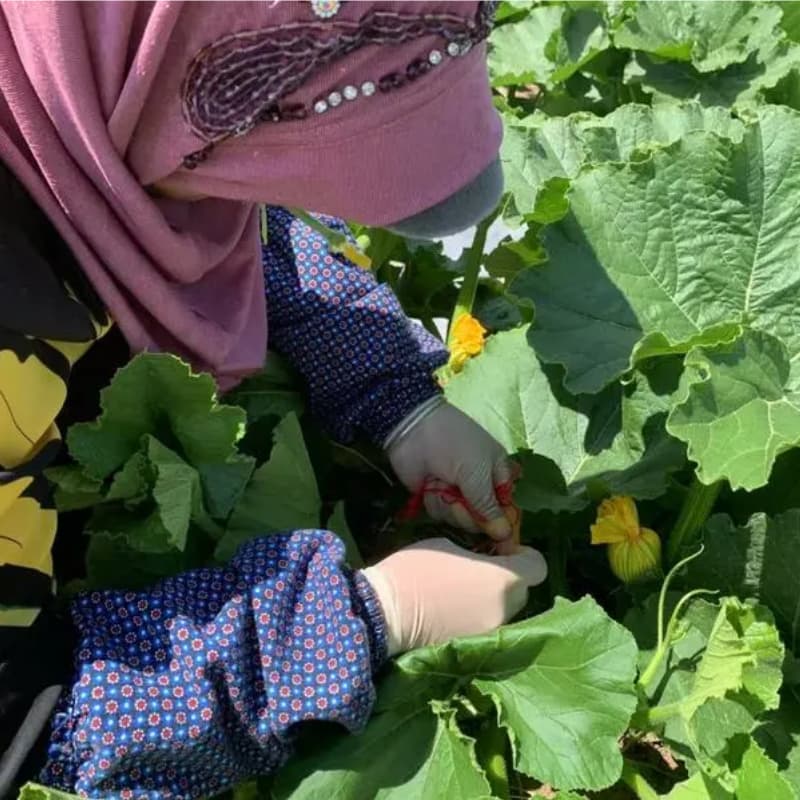

Higher Yields and Uniform Fruits
Hybrid zucchini and melon plants are bred for productivity. Farmers benefit from consistent fruit size, weight, and quality—important for both fresh markets and export.
Stronger Disease and Pest Resistance
Many hybrid seeds are bred to resist diseases like powdery mildew, fusarium wilt, mosaic viruses, and anthracnose. This reduces pesticide use and ensures better harvest stability.
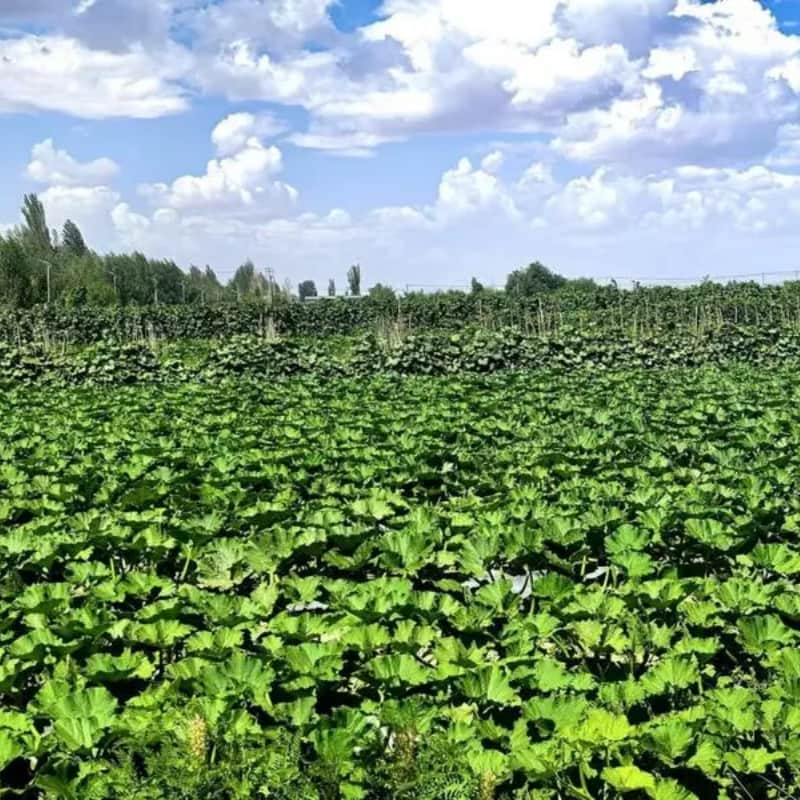

Better Adaptability to Diverse Climates
Hybrid zucchini and melon seeds thrive in regions ranging from Asia to the Middle East, adapting to hot summers, semi-arid areas, and greenhouse cultivation.
Improved Shelf Life and Market Value
Hybrid melons often have longer shelf life and better sugar retention, while hybrid zucchinis maintain firmness and color during transport. This gives farmers a marketing advantage.

Challenges and Solutions in Cross-Pollination
Maintaining Seed Purity
One of the greatest challenges is preventing unwanted cross-pollination from surrounding fields. Isolation distances and controlled pollination practices are critical.
Dependence on Pollinators and Environment
Environmental factors like rainfall, temperature, and pollinator activity directly affect seed production. Using manual pollination techniques can reduce risks.

Common Mistakes in Hybrid Seed Production
- Inadequate isolation from other cucurbit crops
- Pollinating flowers at the wrong stage
- Improper storage of harvested seeds
By following strict field management practices, seed producers can minimize these risks.

Applications and Market Opportunities
Hybrid Zucchini Seeds in Global Markets
Hybrid zucchini is popular in Europe, the Middle East, and Asia, where farmers demand uniform, disease-resistant crops with strong market appeal.
Hybrid Melon Seeds in Middle East and Asia
The Middle East has a strong demand for sweet, high-Brix melons. Hybrid melon seeds from controlled cross-pollination deliver excellent sweetness (Brix 14–18+), uniform rind patterns, and extended shelf life—perfect for export.

Growing Demand for High-Quality Hybrid Seeds
With global population growth, the demand for high-yield hybrid vegetable seeds continues to rise. Seed suppliers who can guarantee purity and consistency, such as Luteseeds, are well-positioned in international markets.
Best Practices for Seed Producers
Field Management for Cross-Pollination Success
- Ensure clean fields free of volunteer plants.
- Monitor pollination progress daily.
- Keep detailed records of parent lines.

Storage, Testing, and Germination Standards
After harvest, hybrid zucchini and melon seeds must be:
- Dried and cleaned
- Tested for purity and germination rates (Luteseeds ensures over 95% germination)
- Stored in cool, dry conditions for maximum shelf life
Tips for Farmers: Trial Planting in New Regions
For farmers in new markets, it’s recommended to start with small-scale trials before large-scale promotion. This ensures the hybrid variety performs well under local climate and soil conditions.

Conclusion
Cross-pollination is the heart of hybrid zucchini and melon seed production. By carefully selecting parent lines, controlling pollination, and maintaining purity, seed producers create varieties that offer farmers:
- Higher yields
- Better disease resistance
- Superior fruit quality
- Stronger market value
As global agriculture continues to evolve, hybrid seeds—powered by cross-pollination—will remain essential for sustainable food supply.

At Luteseeds, we specialize in high-quality hybrid vegetable seeds, including zucchini and melon varieties tailored for Asia, the Middle East, and international markets. With strict quality control and professional seed production techniques, we are committed to supporting farmers worldwide.